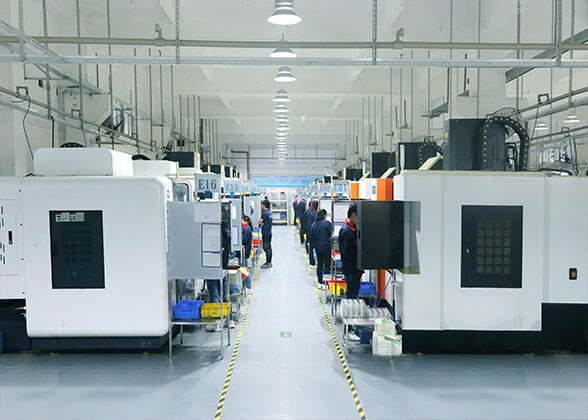
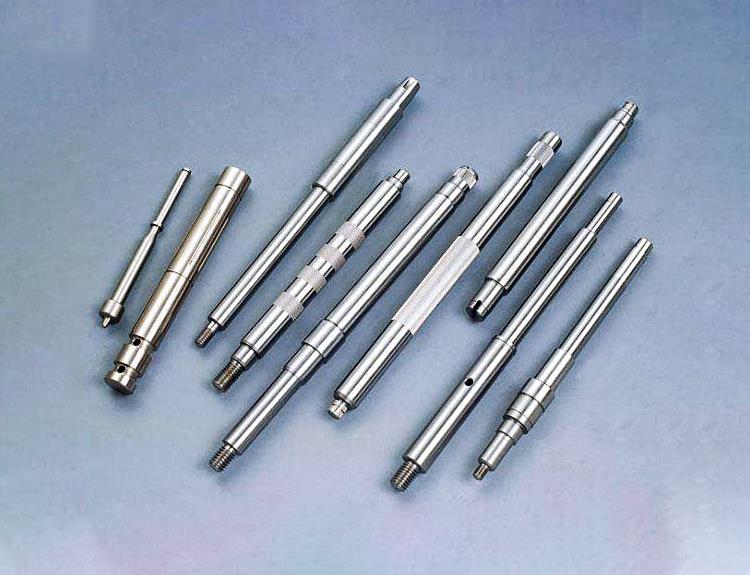
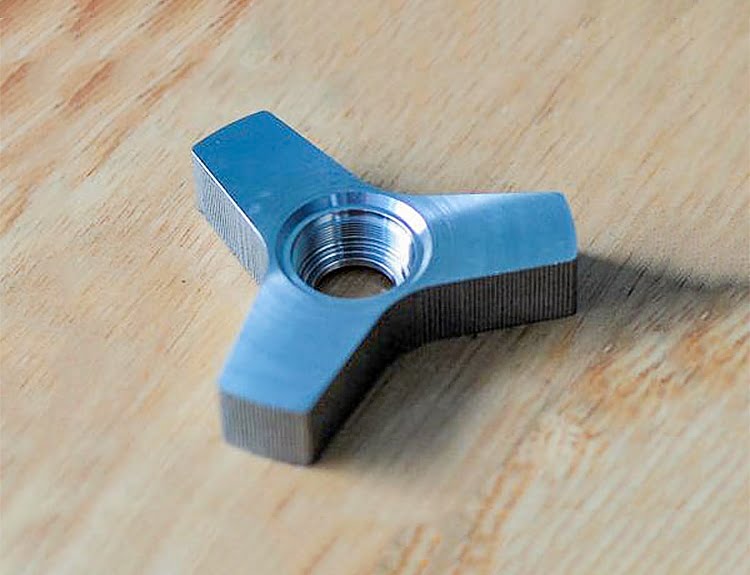
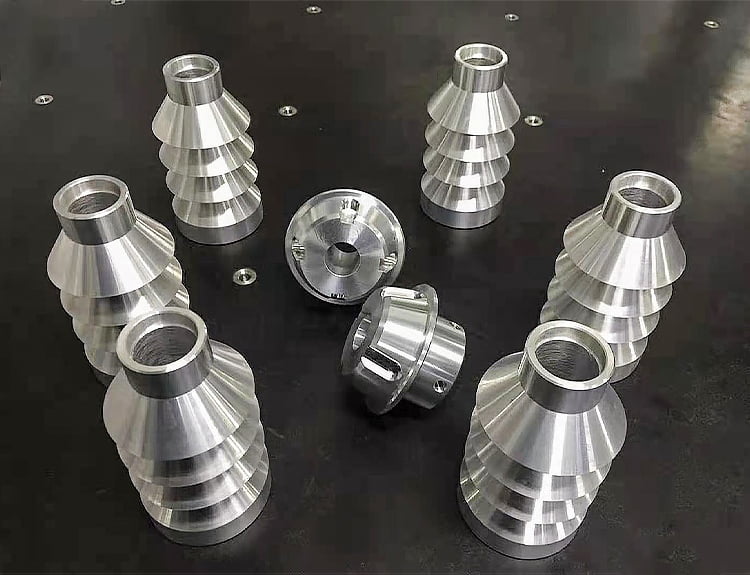
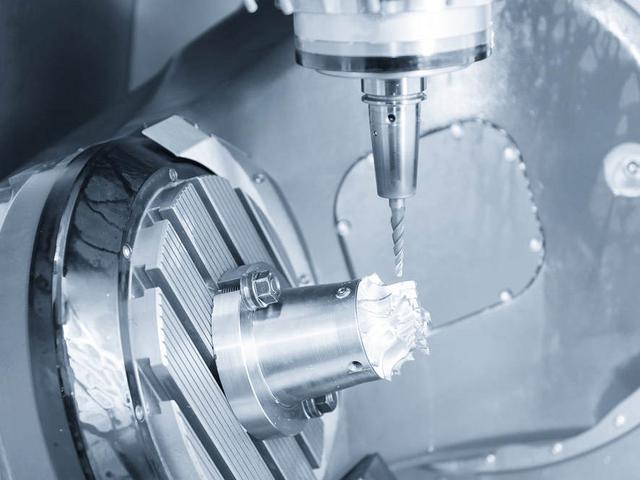
The design of machined parts needs to take into account the design requirements of the machining process for the part. Under the premise of meeting the function, appearance and reliability of the product, the design of machined parts should make the machining process simple, efficient, short processing cycle, low processing cost and high quality.
Due to the above-mentioned characteristics of machining, such as high cost of parts, low processing efficiency, and inability to process complex-shaped parts, machining is being replaced by other processing methods, such as injection processing, stamping processing, and die-casting processing, in more and more industries.
Selection of blanks
Blanks are made according to the required shape of the part, process dimensions, etc. for further processing of the production object.
The type, shape, size and accuracy of the blank have a direct impact on the machining process, product quality, material consumption, processing cycle and manufacturing costs. Therefore, in the design of the product, it is necessary to correctly select the type of blank and determine the shape of the blank.
There are many types of blanks commonly used in machining, and there are many manufacturing methods for the same type of blank.
castings
The shape of complex parts blanks, it is appropriate to use casting methods of manufacture. Most of the current castings with sand casting, which is divided into wooden mold hand molding and metal mold machine molding. Wooden mold hand-shaped castings with low precision, large machining surface allowance, low productivity, suitable for single-piece small batch production or large parts of the casting.
forgings
Mechanical strength requirements of high steel parts, generally to use forging blanks. Forgings are free forging forgings and die forgings of two kinds. Free forging forgings can be manually forged, mechanical hammer forging or press forging and other methods to obtain.
The accuracy of such forgings is low, productivity is not high, the machining allowance is large, and the structure of the parts must be simple; suitable for single and small batch production, as well as the manufacture of large forgings.
The accuracy and surface quality of the forgings are better than that of the free forgings, and the shape of the forgings can be more complex, thus reducing the machining allowance. The productivity of die forging is much higher than that of free forging, but it needs special equipment and forging die, so it is suitable for small and medium-sized forgings with larger batches.
Profile
Profiles can be divided into: round steel, square steel, hexagonal steel, flat steel, angle steel, channel steel and other special cross-sectional profiles according to the shape of the section. Profiles have two types of hot-rolled and cold-drawn. Hot-rolled profiles have low precision, but are inexpensive and used for general parts blanks; cold-drawn profiles are smaller in size and high in precision, easy to realize automatic feeding, but higher in price, mostly used for larger batch production and suitable for automatic machine processing.
Welded parts
Welded parts are obtained by welding method, the advantages of welded parts are simple manufacturing, short cycle time, material savings, the disadvantage is poor vibration resistance, deformation, need to be processed by aging before mechanical processing.
In addition, there are stamping parts, cold extrusion parts, powder metallurgy and other blanks.