I. Introduction
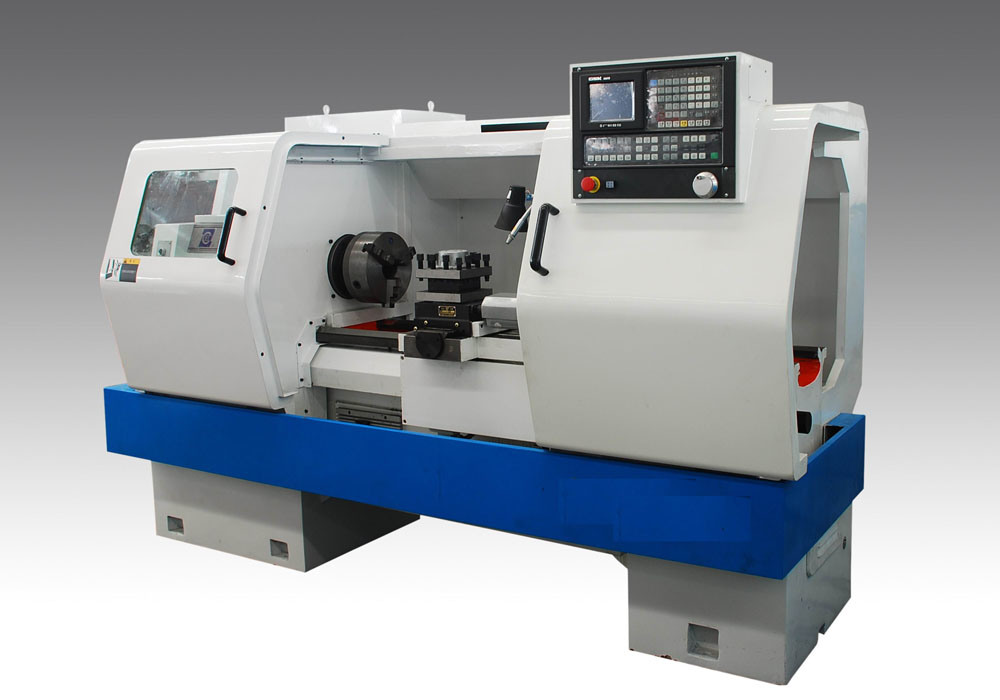
A CNC lathe is a computer-controlled machine tool that is designed to cut, shape, and form metal or other materials turned on a lathe. It is controlled by a computer that reads instructions from a program and moves the cutting tool according to those instructions. CNC lathes are widely used in manufacturing operations where precision is essential, such as the aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries. The use of CNC lathes can lead to increased efficiency, reduced production time, and improved accuracy compared to traditional lathe techniques.
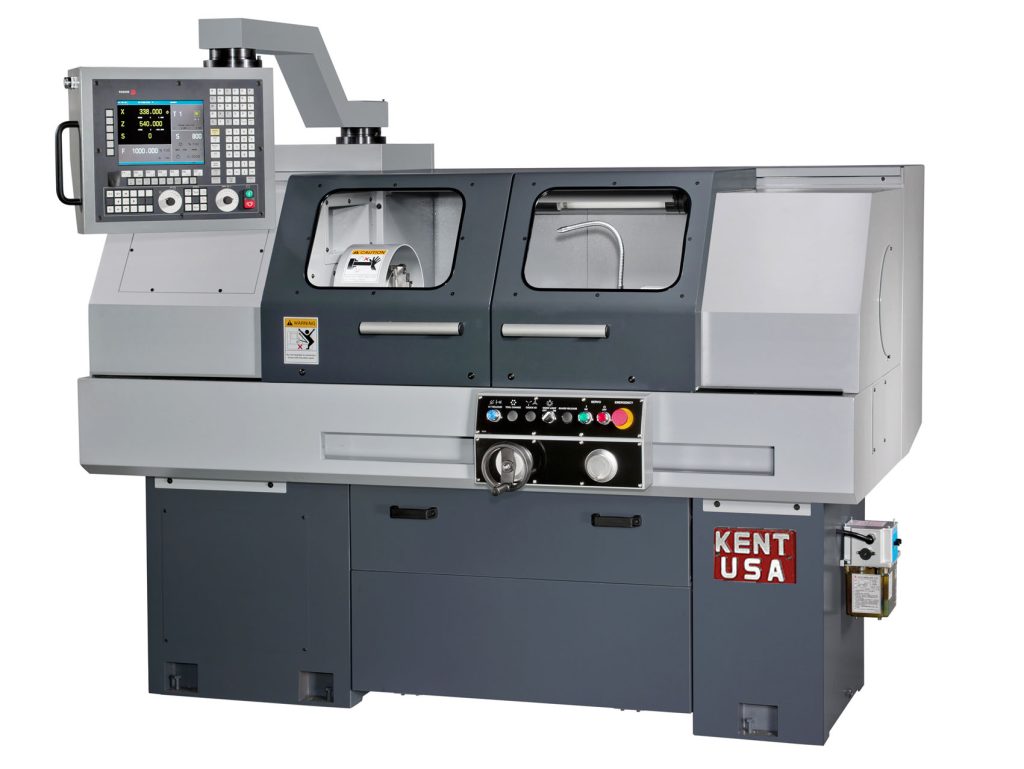
II. CNC Lathe Parts and Components
Headstock:Headstock is the component at the front of the lathe that holds the workpiece and revolves it in a circular motion.
Bed:The Bed is the foundation of the lathe machine on which all other components are mounted.
Tailstock:The Tailstock is the component located at the rear end of the lathe that provides support to the workpiece and helps to align it for cutting operations.
Chuck:The Chuck is the component that grips the workpiece tightly and rotates it in a circular motion.
Controls:Controls refer to the operating controls of the lathe machine, such as levers, buttons, and knobs, used to adjust the speed and motion of the machine.
Motors, Clutches and Brakes:Motors, clutches, and brakes are the mechanical components that power and control the movement of the machine. The motor provides power, the clutch engages and disengages the motor, and the brakes stop the rotation of the machine.
III. How CNC Lathes Work
Programming CNC Lathes:Programming CNC Lathes involves writing instructions in a programming language to tell the lathe machine how to process the workpiece. The programming language used in CNC lathe machining is usually G-code.
Cutting Tools and Tool Holders:Cutting Tools and Tool Holders are the components that physically interact with the workpiece to make cuts. The tool holder is used to hold the cutting tool securely in place, while the cutting tool is the component that removes material from the workpiece.
Tool Paths:Tool Paths refer to the route that the cutting tool takes while machining the workpiece. The tool path is generated from the G-code program, and it ensures that the cutting tool removes material from the workpiece accurately and efficiently.
Cutting Parameters:Cutting Parameters are the values that specify how the cutting tool interacts with the workpiece. These parameters include cutting speed, feed rate, depth of cut, and cutting tool orientation. Adjusting the cutting parameters appropriately ensures efficient and precise machining.
IV. Types of CNC Lathes
Slant Bed Lathe:A Slant Bed Lathe is a type of lathe machine with a slanted bed that enables faster chip removal, improves tool life and accuracy, and enhances overall machine rigidity. This type of lathe is commonly used in the production of complex and high-precision components.
Flat Bed Lathe:A Flat Bed Lathe is a type of lathe that has a flat, horizontal bed, and the cutting tools move along the bed’s axis. They are often used for smaller parts in high volume applications.
Swiss Lathe:A Swiss Lathe is used primarily for small, intricate parts due to its high precision and accuracy. The workpiece is fed through a guide bushing, and the cutting tool moves along with the workpiece axis.
Vertical Lathe:A Vertical Lathe, also known as a VTL, has a vertical axis and the workpiece rotates on a horizontal axis. This type of lathe is typically used for large and heavy parts, such as turbines or gears.
Hybrid Lathe:A Hybrid Lathe combines the advantages of both CNC milling and turning machines in a single unit, allowing for multiple cutting operations in one setup. It provides more efficient production, improves accuracy and quality, and reduces tooling costs.
V. Advantages of CNC Lathes
Improved Productivity:CNC lathe machines are capable of faster and more precise machining operations compared to traditional manual methods. A CNC lathe can also work continuously without operator intervention, allowing for more efficient production.
Consistency and Accuracy:CNC lathes use a pre-programmed tool path and cutting parameters, which results in consistent and predictable machining quality. This level of accuracy is not possible with manual operation, which can be affected by various factors like operator skill, fatigue, and environmental variables.
Reduced Errors:CNC lathes reduce human error in machining operations. The pre-programmed tool path and cutting parameters help to eliminate operator mistakes, such as incorrect dimensions or tool selection, which leads to better part quality.
Increased Machining Efficiency :CNC lathes machines can perform multiple machining operations on a part in a single setup. This reduces production time, increases efficiency, and reduces machine downtime between operations. It also enables the creation of more complex geometries and shapes that would be challenging or impossible to produce manually.
VI. CNC Lathe Applications
Automotive Industry:CNC lathe machines are used to produce auto parts such as gears, shafts, pistons, and brake discs. CNC lathe machining produces parts that have consistent shape and design specifications, which ensures that parts fit and operate properly.
Aerospace Industry :CNC lathe machines produce precision parts such as complex engine components, turbine parts, and navigation instruments. In the aerospace industry, quality control and precision are critical factors, and CNC lathe machining allows for a high degree of accuracy and consistency.
Medical Equipment Industry:CNC lathe machines are used to manufacture medical devices such as surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. The consistent quality and accuracy achieved through CNC lathe machining are essential in the medical industry, where precision is a top priority.
Electronics Industry:CNC lathe machines manufacture electrical components such as connectors, switches, and terminal blocks. CNC lathe machining can produce precision parts with tight tolerances, enabling the creation of smaller and more efficient electronic devices.
VII. CNC Lathe Safety
General Safety Measures
Machine Guarding: Always ensure that the machine is guarded by appropriate safety guarding to prevent accidental contact with the machine’s rotating parts, chips or fluid ejection.
Spindle Lockout:Before making any changes to the cutting tool or workpiece, lockout and tag out the machine to prevent any accidental startup.
Chip Management:Follow proper chip management to avoid a build-up of chips and debris in the workspace. Improper chip management can cause damage to the workpiece, machine components or cause injuries to the operator.
Tool Selection:Select the appropriate cutting tool for the job and ensure it’s properly installed with the correct orientation and tightened to ensure it stays in place.
Work Holding: Properly secure the workpiece in place to prevent it from being dislodged or ejected from the machine during machining.
Lubrication:Keep the machine properly lubricated, but ensure any spilled or excess lubricants are promptly cleaned.
CNC Lathe Specific Safety Precautions
Emergency Stop:lways ensure the emergency stop button is within easy reach and is in proper working order in case an emergency arises.
Personal Protective Equipment :Wear appropriate personal protective equipment such as safety shoes, safety glasses and hearing protection to avoid serious injuries caused by exposure to flying chips or debris, machine-generated noise pollution or strain.
By following these CNC lathe specific safety precautions in addition to the general safety measures, workplace accidents and injuries could be minimized.
VIII. Future of CNC Lathes
Advancements in Technology and Industry Trends
Smart Manufacturing:CNC Lathes are becoming connected to the internet and can communicate with each other, suppliers, and managers. This helps to increase machine uptime and production efficiency.
3D Printing and Additive Manufacturing :the introduction of 3D printing and additive manufacturing technologies have enabled automated prototype development, thus accelerating the manufacturing process.
Artificial Intelligence: AI and machine learning technology aim to learn from machine data to avoid potential problems and optimize cutting tool and machine performance.
Robotic Automation: the use of robots in CNC lathe machining automates tasks, which enhances productivity and reduces lead times from design to finished product.
Hybrid Production:hybrid capabilities of CNC lathe machines which allow switching between subtractive manufacturing and additive manufacturing on the same machine, ushering tremendous production improvements.
Miniaturization:CNC Lathes are now capable of producing smaller and more complex parts with high precision, increasing efficiency and productivity.
These advancements and industry trends have given rise to increased efficiency, cost-saving, greater accuracy and quality in CNC lathe machining while enabling the production of intricate designs and shapes that were previously impossible with traditional.

IX. Conclusion.
In conclusion, CNC lathe machining is a highly effective and efficient method used in the manufacturing of a wide range of products in different industries. CNC lathe machines provide a high degree of accuracy, consistency, and precision that are critical in various industries such as aerospace, automotive, medical equipment, and electronics.Recent advancements in technology, such as smart manufacturing, artificial intelligence, and robotic automation have immensely impacted CNC lathe machining, improving productivity, efficiency, and cost-savings while enabling the production of highly complex and intricate parts.
Overall, CNC lathe machining technology has positively impacted manufacturing processes through increased efficiency, accuracy, safety and flexibility, enabling customization and better quality control, resulting in highly satisfactory end products.