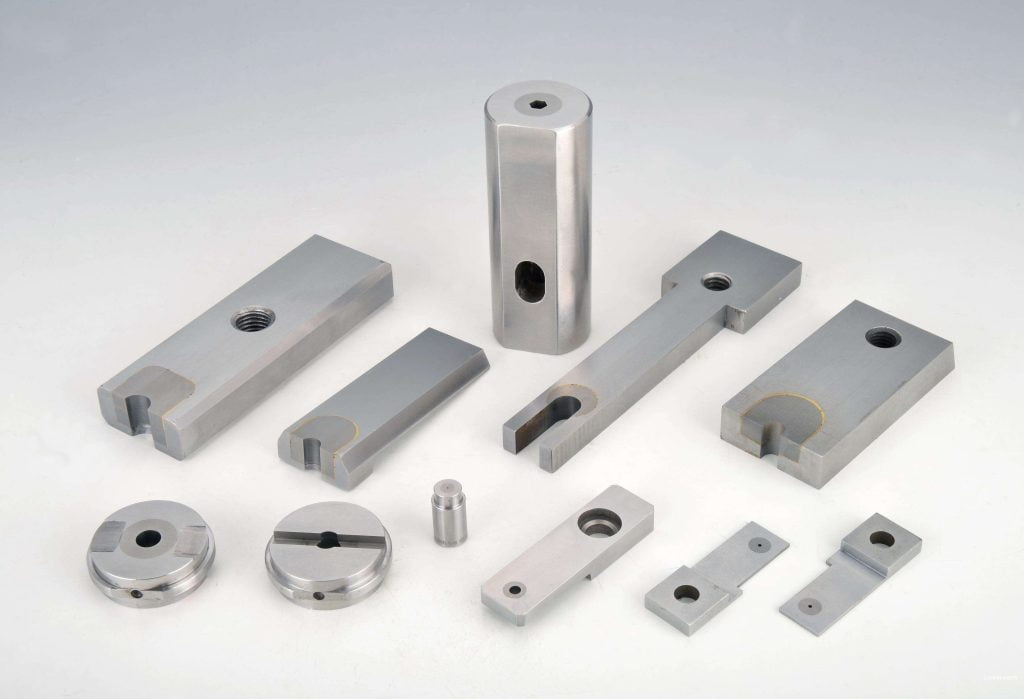
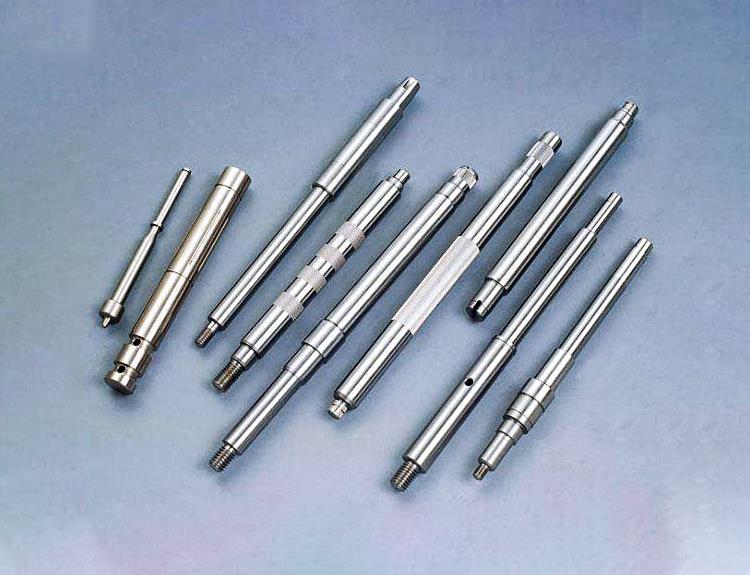
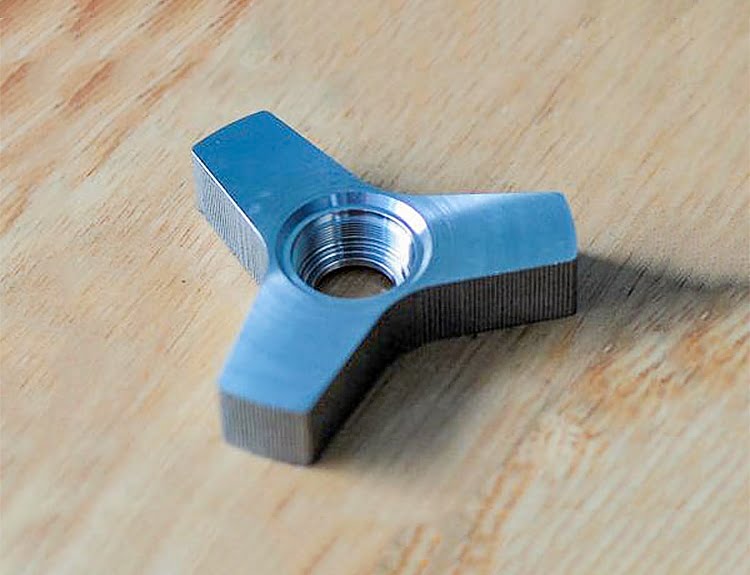
The plastic processing of the deformed magnesium alloy is roughly the same as that of the deformed aluminum alloy, but the magnesium alloy is generally heated, and the ingot can be heated in a similar way to that of the aluminum alloy.
The ingot must not be in direct contact with the flame, otherwise it will burn and cause a catastrophic fire which is not easy to control. It is best to remove the mechanical burr on the ingot so as not to cause fire.
Usually, the box-type resistance furnace is used for heating. The magnesium alloy has high thermal conductivity, and the ingot of any shape and size can be heated directly in the furnace without preheating.
Because the heating temperature of magnesium alloy is much lower than its melting point, it is not necessary to use inert gas or reducing atmosphere during heating, but it is necessary to ensure that the furnace temperature is uniform and large temperature gradient is not allowed. It is better to use forced circulation air flow.
At the same time, the heating furnace should be guaranteed to control the temperature accurately, and the ingot heating protection measures should be taken to prevent overheating or even combustion.
Plastic processing technology
The processing technology of deformed magnesium alloy is similar to that of deformed aluminum alloy, which can be divided into integral forming process and secondary forming process. Secondary forming refers to the further processing of semi-finished products such as bending, stamping, extrusion, finishing pressing and spinning.
Forming by rolling
At room temperature, the plasticity of magnesium alloy is very low and it is not suitable for cold rolling. Therefore, hot rolling and warm rolling are carried out at a certain temperature to produce thick and thin strip. The magnesium alloys suitable for strip production are MG-Mn alloys.
Most magnesium is produced by an extrusion process. The products are tubes, rods and shapes, and the extrusion process is carried out at a certain temperature. The extrusion process and equipment of magnesium alloy are similar to that of aluminum alloy extrusion material
At present, hot extrusion is the primary plastic deformation processing technology of deformed magnesium alloy. Like the extrusion of deformed aluminum alloy, magnesium alloy extrusion material can be extruded forward or reverse. It can be produced by single action extruder, double action extruder, horizontal extruder or vertical extruder.
About temperature
Forging and pressing deformation magnesium alloy can not be cold section, can only be hot forging, forging temperature of 200℃~400℃, not higher than 400℃, otherwise serious oxidation will occur, and grain size will grow.
The thermal conductivity of magnesium alloy is high, about 80W, almost twice that of steel. At the same time, due to the low density and low heat capacity of magnesium alloy, it will soon cool down after contacting the die, and the deformation resistance will increase and the filling capacity will decrease. This magnesium alloy is suitable for isothermal forging.
Superplastic forming
Superplastic forming is a process in which sheet metal is used to process parts under superplastic conditions. Some deformed magnesium alloys have superplasticity under certain conditions and can be made into complex parts at one time. The fine grain AZ31, AZ61 and ZK60 alloys all have superplasticity.
Secondary forming The secondary forming of magnesium alloy semi-finished products includes: superplastic forming, bending forming, deep drawing, hand spinning, strong spinning, rubber sheet forming, drawing forming, drop hammer forming, etc. Magnesium alloys can be formed at room temperature, but most alloys should be heated to a certain temperature. High temperature forming has special requirements for die and process.