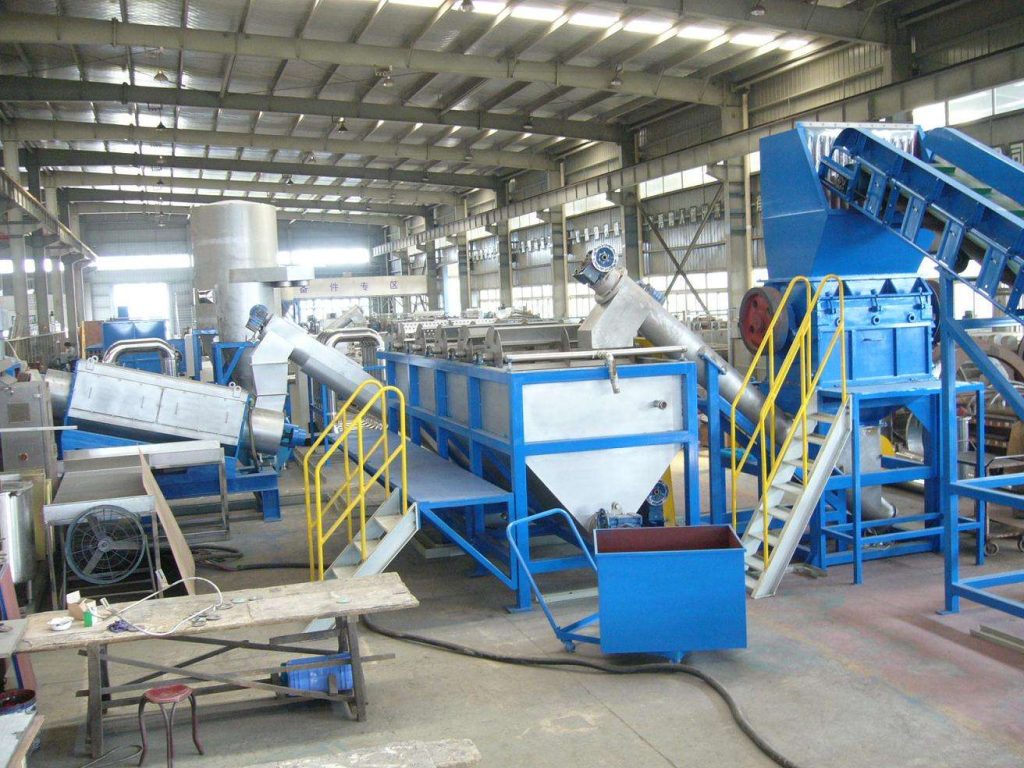
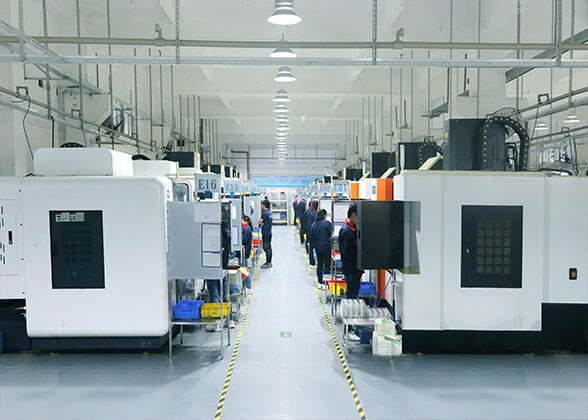
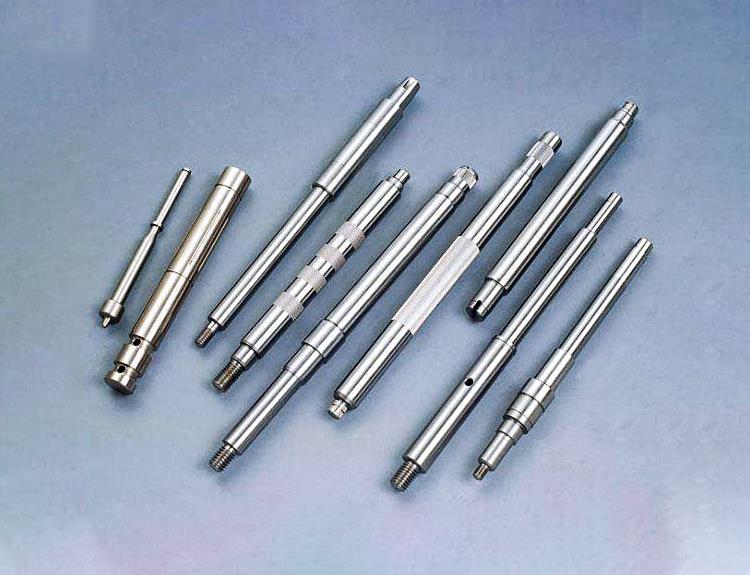
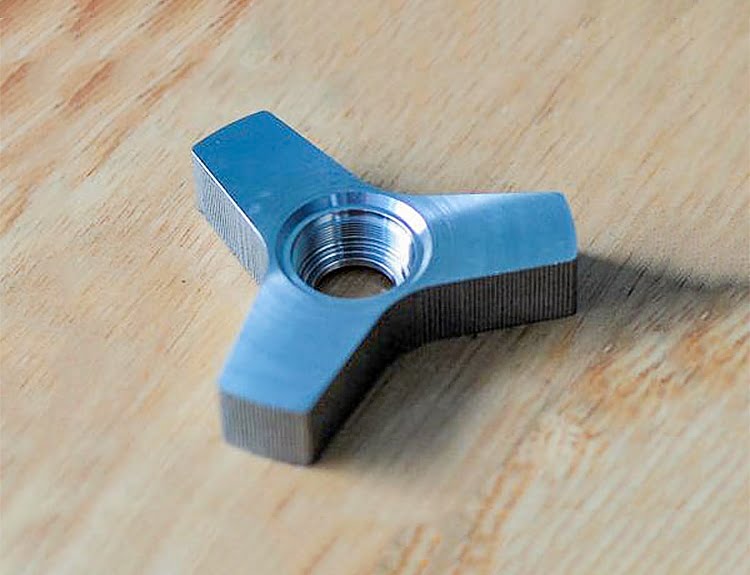
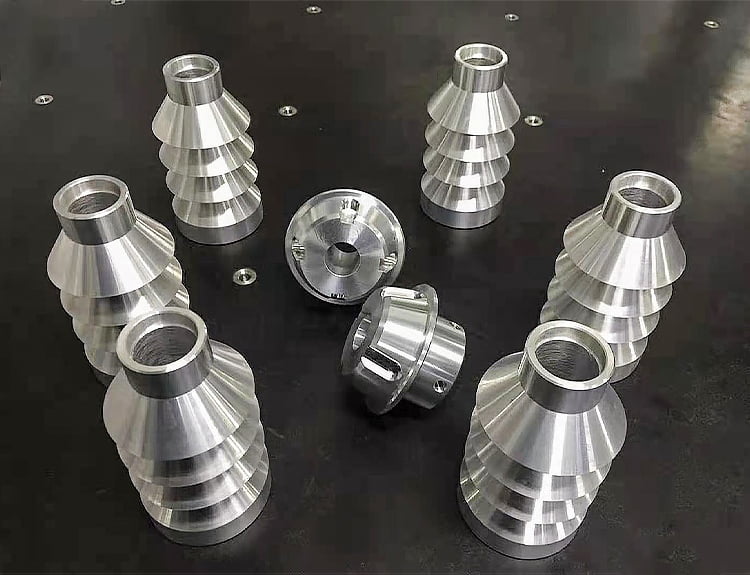
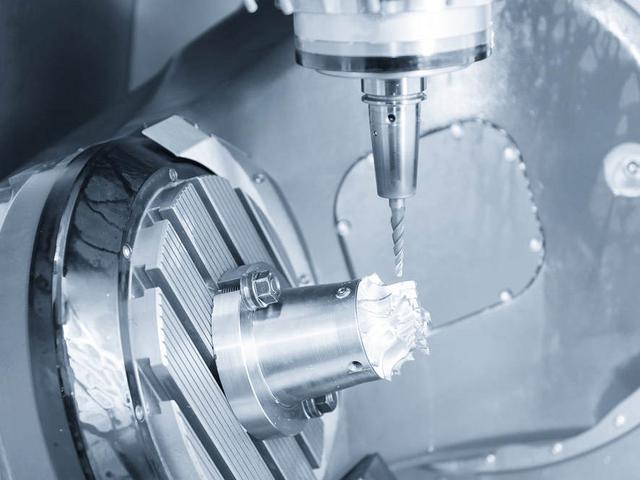
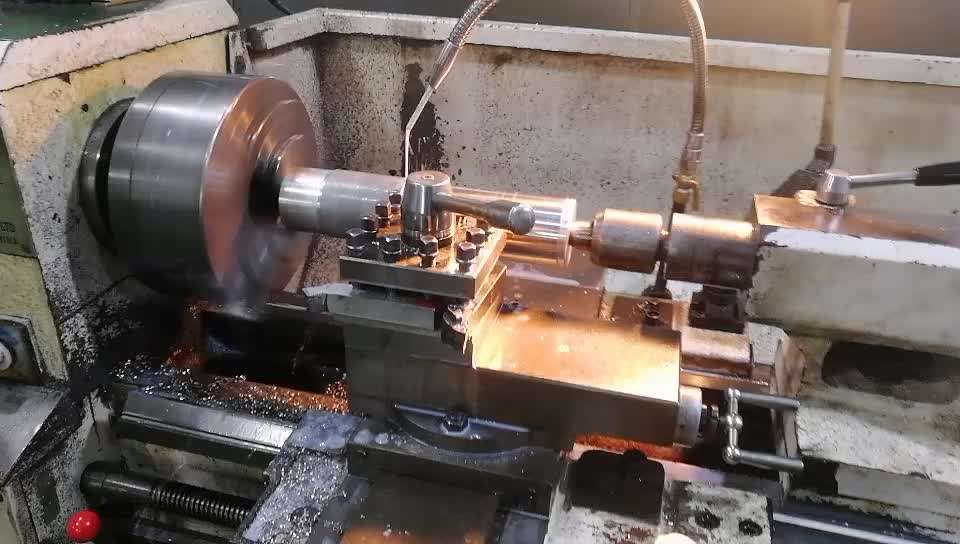
Material quality mechanical parts processing
The material removal manufacturing process is to cut off excess materials from the workpiece in a certain way to obtain the required shape and size parts. Such processes require sufficient excess material on the workpiece surface. In the process of material removal, the workpiece gradually approximates the shape and size of the ideal part. The greater the difference between the shape and size of raw materials or blanks and zero h, the more materials will be removed, the greater the material loss, and the more energy will be consumed during processing. Sometimes the volume of material consumed even exceeds the volume of the part itself.
Although the material utilization rate of material removal process is low, it is still the main means to improve the quality of parts, and also has a strong processing adaptability. The combination of material removal process and material forming process can greatly reduce the consumption of raw materials. With the development of less and no cutting technology (precision casting, precision forging, etc.), the utilization of materials can be further improved. When the production quantity is small, in order to reduce the investment in the material forming process, it is economical and reasonable to simply use the material removal process.
The material removal process has many processing forms, including traditional cutting and special processing.

Material forming and quality mechanical parts processing
Casting
Casting is the process of pouring liquid metal into the mold cavity that is suitable for the shape and size of the part, and obtaining the blank or part after cooling and solidification. The basic technological processes are molding, smelting, pouring, cleaning, etc. Due to the influence of filling capacity, shrinkage and other factors during alloy casting, the castings may have uneven structure, shrinkage cavity, thermal stress and deformation, resulting in low precision, surface quality and mechanical properties. However, due to its strong adaptability and low production cost, casting is still widely used. The blank of parts with complex shape, especially complex inner cavity, is often cast.
At present, the common casting methods in production include ordinary sand mold casting, investment casting, metal mold casting, pressure casting, casting, centrifugal casting, etc. Among them, ordinary sand casting is the most widely used.
Forging and pressing
Forging and sheet metal stamping are collectively referred to as forging. Forging is to use forging equipment to apply external force to the heated metal for plastic deformation to form a blank with a certain shape, size and microstructure. The internal structure of the forged blank is dense and uniform. The metal streamline distribution is reasonable, and the strength of the parts is improved. Therefore, forging is often used to manufacture blanks of parts with high requirements for comprehensive mechanical properties.
Forging can be divided into free forging, mold forging and die forging.
Free forging is to place the metal between the upper and lower parts of the iron for metal plastic deformation. The free flowing sand Shangwei 3 has low vorticity and low precision. It is generally used to produce forgings with small batch size and simple shape.
Model forging is to place metal in the die chamber of the forging die to deform. The plastic flow of metal is limited by the die chamber. The forming efficiency is high, the precision is high, and the distribution of metal streamline is more reasonable. However, due to the high cost of mold manufacturing, it is usually used for mass production. The forging force required for forging with the free slightly chirped die is large, so it cannot be used for forging large forgings.

Powder metallurgy
Powder metallurgy is a process that uses metal powder or mixture of metal and non-metal powder as raw materials to manufacture some metal products or metal materials through mold pressing, sintering and other processes. It can not only produce special metal materials, but also produce metal parts with little or no machining. The utilization rate of powder metallurgy wheel can reach 95%, which can greatly reduce the input of cutting and reduce the production cost. Therefore, it is increasingly widely used in machinery manufacturing. Due to the high price of powder raw materials used in powder metallurgy and the poor fluidity of powder during forming, the shape and size of parts are limited. There are a certain amount of micro pores in the powder metallurgy parts, whose strength is about 20%~30% lower than that of castings or forgings, and its plasticity and toughness are also poor.