I. Introduction
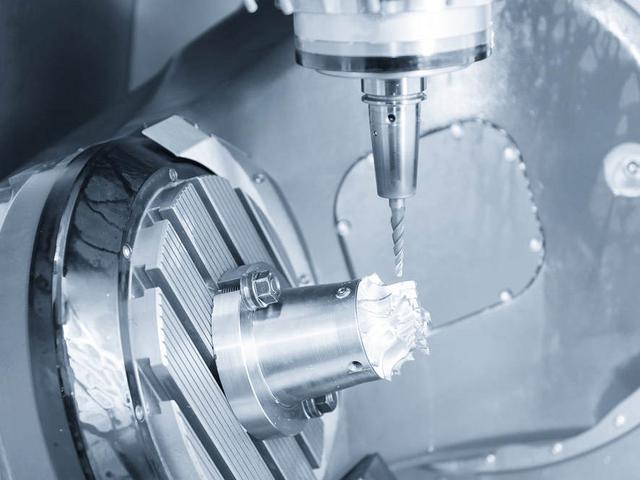
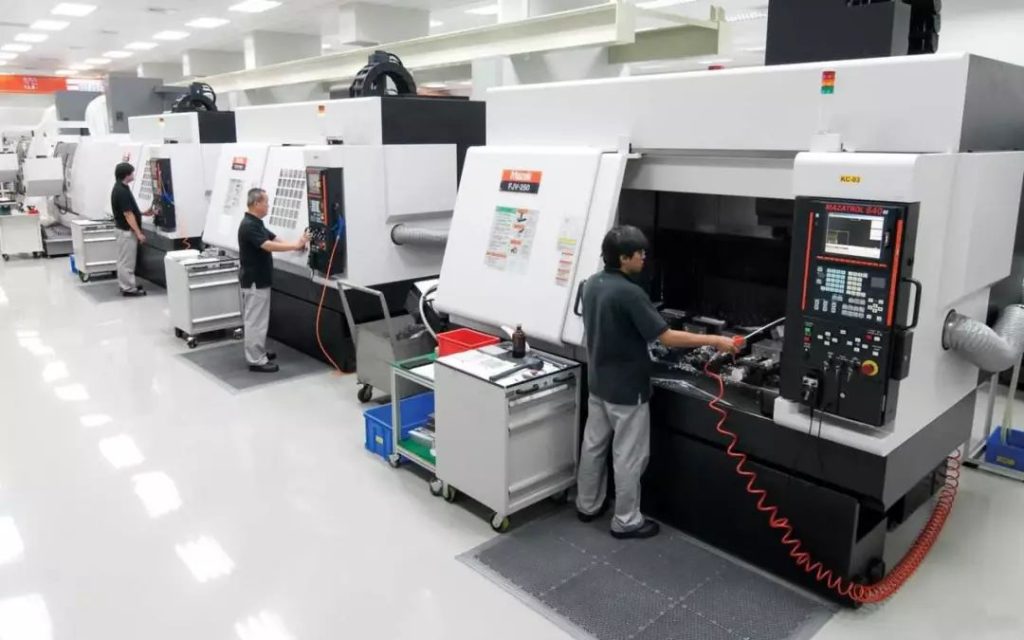
Metal CNC machining is the process of using computer-controlled machines to remove material from a metal workpiece to create a desired shape or product. CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control, and it refers to the use of a computer program to control the movement of the machining tools.
Metal CNC machining is important in manufacturing because it allows for high precision and accuracy, as well as the ability to produce complex parts with tight tolerances. It is also faster and more efficient than traditional machining methods, which helps to reduce production costs and increase productivity. Metal CNC machining is used in a wide range of industries, from aerospace and automotive to medical devices and electronics.
II. Basics of Metal CNC Machining
Understanding CNC Machines:
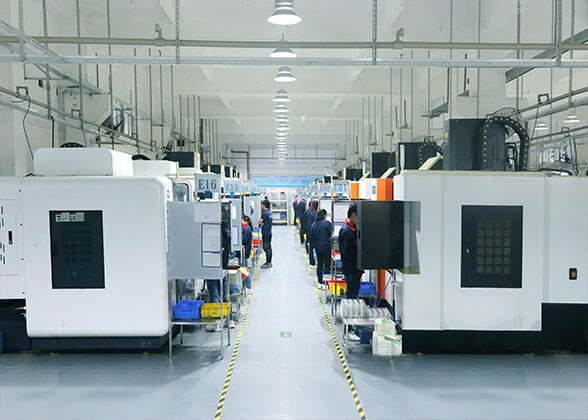
CNC machines are advanced manufacturing tools that use computer programs to control their movement and operation. They consist of several key components, including a control unit, servo motors, drive system, and machining tools. The control unit reads the instructions from a computer program and translates them into movements for the machine’s motors and machining tools.
Types of CNC Machines Used for Metal Machining:
There are several types of CNC machines used for metal machining, including:
- CNC milling machines: used for cutting and shaping solid metal workpieces
- CNC turning machines: used for creating cylindrical shapes by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool
- CNC drilling machines: used for creating holes in metal workpieces
- CNC grinding machines: used for precision grinding and finishing operations
- CNC EDM machines: used for removing metal by a controlled spark between an electrode and the workpiece
CNC Programming Basics:
CNC programming involves creating a set of instructions that the machine will follow to produce a desired part. This is typically done using specialized software that allows the programmer to specify the tool path, cutting speed, feed rate, and other parameters. The program is then transferred to the CNC machine’s control unit, which reads and executes the instructions to produce the part. Programming requires knowledge of the machining process and the specific capabilities of the machine being used.
III. Techniques in Metal CNC Machining
1.Milling: Milling is a technique used to remove material from a workpiece using rotating cutting tools. The workpiece is held in place while the cutting tool rotates and removes material from the surface, creating the desired shape.
2.Turning: Turning is a technique used to create cylindrical shapes by rotating the workpiece against a cutting tool. The cutting tool moves along the length of the workpiece, removing material to create the desired shape.
3.Drilling: Drilling is a technique used to create holes in metal workpieces. The CNC machine uses a rotating drill bit to remove material and create a hole in the workpiece.
4.Grinding: Grinding is a technique used for precision grinding and finishing operations. It involves using an abrasive wheel to remove material from the workpiece and create a smooth, polished surface.
5.EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): EDM is a technique used for cutting and shaping hard metals that are difficult to machine with traditional methods. It involves using a controlled spark between an electrode and the workpiece to remove material and create the desired shape.
6.Laser Cutting: Laser cutting is a technique used to cut and shape metal workpieces using a high-powered laser beam. The laser beam melts or vaporizes the material, creating a precise cut or shape.
IV. Applications of Metal CNC Machining
Metal CNC machining has a wide range of applications in various industries, including:
1.Aerospace: CNC machining is used to create complex parts for aerospace applications, such as aircraft engines, landing gear, and airframes. The precision and accuracy of CNC machining make it essential for producing parts that meet the stringent safety and performance requirements of the aerospace industry.
2.Automotive: CNC machining is used to create parts for automotive applications, such as engine components, suspension systems, and brake parts. The speed and efficiency of CNC machining make it a cost-effective way to produce high-quality parts for the automotive industry.
3.Medical Devices: CNC machining is used to create parts for medical devices, such as surgical instruments, implants, and prosthetics. The precision and accuracy of CNC machining make it essential for producing parts that meet the strict safety and regulatory requirements of the medical industry.
4.Electronics: CNC machining is used to create parts for electronic devices, such as computer components, circuit boards, and connectors. The ability to produce small, precise parts makes CNC machining essential for the electronics industry.
5.Defense and Military: CNC machining is used to create parts for defense and military applications, such as weapons systems, aircraft components, and communication equipment. The precision and accuracy of CNC machining make it essential for producing parts that meet the strict requirements of the defense and military industry.
6.Energy and Power: CNC machining is used to create parts for energy and power applications, such as turbines, generators, and power transmission equipment. The ability to produce high-strength, high-precision parts makes CNC machining essential for the energy and power industry.
V. Advancements in Metal CNC Machining
Metal CNC machining is constantly evolving, and there have been significant advancements in recent years that are driving the industry forward. Some of the key advancements in metal CNC machining include:
Automation and Robotics: Automation and robotics are increasingly being integrated into metal CNC machining processes, enabling manufacturers to improve efficiency, reduce errors, and increase production capacity. This has led to the development of “lights out” manufacturing facilities, where CNC machines can operate autonomously 24/7.
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) are being used to optimize CNC machining processes, improving efficiency and reducing costs. By analyzing data from sensors and other sources, AI and ML algorithms can identify patterns and make predictions about the machining process, enabling manufacturers to make data-driven decisions.
Industry 4.0 and Digital Manufacturing: Industry 4.0 refers to the trend of integrating digital technologies into manufacturing processes, enabling manufacturers to create “smart factories” that are more efficient, flexible, and connected. Digital manufacturing technologies, such as additive manufacturing and cloud-based software platforms, are increasingly being used alongside CNC machining to create more agile and responsive manufacturing operations.
These advancements are driving the metal CNC machining industry forward and are enabling manufacturers to produce higher-quality parts more efficiently than ever before.
VI. Choosing the Right Metal CNC Machining Service Provider
CNC Milling Services
1.China Top CNC Milling Supplier & Manufacturer – V1 Machining offers worldwide clients affordable, rapid, high precision custom CNC Milling Services, variety of materials available to meet the needs of different industries!
- Machined prototypes in as fast as 1 days.
- 50+metals and plastics
- Tolerances down to +-0.001mm
- ISO 9001:2015、ISO 14001:2015 and IATF 16949
2.Factors to consider when selecting a machining partner:
Expertise: Choose a machining partner with extensive experience in your industry and with the type of parts you need to produce. Check their track record of successfully completing projects similar to yours.
Equipment and Technology: Ensure that your machining partner has the right equipment and technology to produce the parts you need to your exact specifications. Ask about the types of CNC machines they use and their capabilities.
Quality Control: Verify that your machining partner has a robust quality control process in place, including inspection and testing procedures. Look for certifications or accreditations, such as ISO 9001, to ensure that they adhere to industry standards.
Pricing and Lead Time: Obtain quotes from multiple machining partners to compare pricing and lead times. Be wary of low-priced providers who may sacrifice quality to offer a lower price.
Communication and Collaboration: Choose a machining partner who communicates clearly and regularly with you throughout the project. They should be open to collaborating with you on design and engineering issues and provide regular progress updates.
3.Questions to ask when evaluating a service provider
What types of CNC machines do you use, and what are their capabilities?
Do you have experience producing parts for my industry and application?
What is your quality control process, and do you have any certifications or accreditations?
What is your pricing structure, and what is the lead time for production?
How do you communicate with your clients throughout the project, and what is your project management process?
Can you provide engineering and design support if needed?
Choosing the right metal CNC machining service provider requires careful consideration of these factors and thorough evaluation of potential partners.

VII. Conclusion
In conclusion, metal CNC machining is a vital component of modern manufacturing, allowing for the precise production of complex metal parts across a range of industries. CNC machines and programming have revolutionized the industry, providing faster and more accurate production capabilities than ever before.
The techniques used in metal CNC machining, such as milling, turning, drilling, grinding, EDM, and laser cutting, each have their own unique advantages and are selected based on the specific requirements of the project.
Recent advancements in automation, robotics, artificial intelligence, and digital manufacturing have further expanded the capabilities of metal CNC machining, improving efficiency and productivity while maintaining high levels of quality control.
When choosing a metal CNC machining service provider, it is essential to consider factors such as expertise, equipment and technology, quality control, pricing and lead time, and communication and collaboration. Asking the right questions can help ensure that you select the right partner for your project.
Looking ahead, the future outlook for metal CNC machining is bright, with continued advancements in technology and automation set to transform the industry even further. As the demand for precision metal parts continues to grow across various industries, CNC machining will continue to play a critical role in driving innovation and progress.