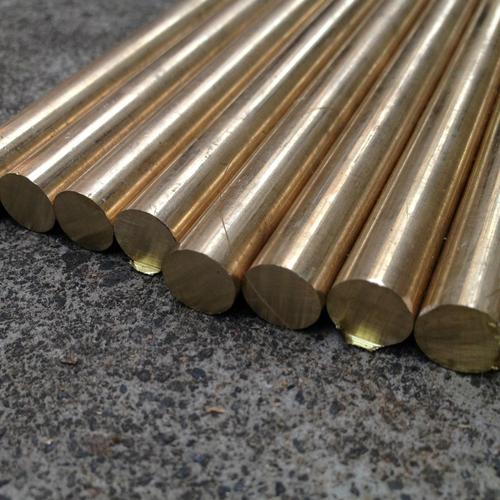
Red copper and brass are two metal materials that are often mixed together. When the two metals are placed side by side, you can notice that copper and brass look a little similar. However, there is a slight difference in color.
Copper is one of the earliest metals discovered, processed and utilized by human beings. This is because copper exists in its natural state. This pure metal was used to make tools, weapons and decorations in prehistoric times. It is a kind of pure metal that is directly suitable for processing, which is different from the manually made brass. Copper can be used alone or combined with other alloys and pure metals to form a subset of alloys.
Red copper and brass are two metal materials that are often mixed together. When the two metals are placed side by side, you can notice that copper and brass look a little similar. However, there is a slight difference in color.

What is brass in brass machined parts?
What is red copper and brass? What is the difference between them?
In business, there are many kinds of metals, which has caused many discussions in the manufacturing industry. These arguments are due to the inability of metal users to distinguish between various metal materials. Especially when the difference is very subtle.

Red copper and brass are two metal materials that are often mixed together. When the two metals are placed side by side, you can notice that copper and brass look a little similar. However, there are slight differences in color, and it requires a lot of expertise to distinguish between the two. To avoid using the wrong choices in your project, reading them may be critical to a successful project. This article will explain these problems in detail to determine the difference between red copper and brass.
First of all, let's know what is brass and red copper?
What is red copper?
Copper is one of the earliest metals discovered, processed and utilized by human beings. This is because copper exists in its natural state. This pure metal was used to make tools, weapons and decorations in prehistoric times. It is a kind of pure metal that is directly suitable for processing, which is different from the manually made brass. Copper can be used alone or combined with other alloys and pure metals to form a subset of alloys.
Copper is composed of elements with high conductivity and heat conductivity. In its purest form, it is soft and malleable. For thousands of years, it has been used as a building element and building material of other alloys.

What is brass?
Brass is a copper alloy containing a certain amount of zinc. Therefore, this metal is often mistaken for copper. In addition, brass is composed of other metals such as tin, iron, aluminum, lead, silicon and manganese. The addition of these other metals contributes to a more unique combination of characteristics. For example, the content of zinc in brass is helpful to improve the ductility and strength of brass based copper materials. The higher the zinc content in brass, the stronger the flexibility of the alloy. In addition, according to the amount of zinc added, its color can also vary from red to yellow.
Brass is mainly used for decoration because it is similar to gold. In addition, because of its durability and processability, it is often used for making musical instruments.
The two metals can be distinguished according to their elemental composition. As we said before, copper is a pure base metal, which is an element with high conductivity. Its electronic structure is similar to that of silver and gold. As a metal, brass is an alloy of copper and zinc. Unlike copper, it contains many elements according to its alloy form. The common element composition of brass includes its main components copper (Cu) and zinc (Zn), but according to its alloy form, it may have the following components:

Corrosion resistance
Corrosion can also be used to distinguish between the two metals. These two metals do not contain iron, so they are not easy to rust. After a period of oxidation, copper will form green verdigris. This prevents further corrosion of the copper metal surface. However, brass is an alloy of copper, zinc and other elements and can also resist corrosion. In conclusion, compared with copper, brass has a more golden color and stronger corrosion resistance.

conductivity
The difference in conductivity of various metals is often not understood. However, assuming the conductivity of one material, because it looks similar to another conductive material of known capacity, this may be disastrous for the project. This kind of mistake is more or less obvious in the phenomenon of replacing copper with brass in electrical applications.
In contrast, copper is the conductivity standard for most materials. These measurements are expressed as relative measurements of copper. This means that copper has no resistance and is 100% conductive in an absolute sense. On the other hand, brass is an alloy of copper, and its conductivity is only 28% of that of copper.

thermal conductivity
The thermal conductivity of a material is only a measure of its thermal conductivity. This thermal conductivity varies from metal to metal, so it must be considered when materials need to be used in high temperature operating environment. The thermal conductivity of pure metals remains unchanged with the increase of temperature, while the thermal conductivity of alloys increases with the increase of temperature. In this case, copper is a pure metal, while brass is an alloy metal. In contrast, copper has the highest conductivity.

melting point
The melting point of metal is very important to the selection of engineering materials. This is because component failure may occur at the melting point. When a metal material reaches its melting point, it changes from solid to liquid. At this point, this material can no longer play its role.
Another reason is that metals are easier to form in liquid form. This will help to select the best formability between copper and brass that is required for a project. In metric system, the melting point of copper is 1084 ° C at most, while that of brass is 900 ° C to 940 ° C. The melting range of brass is attributed to different element compositions.
hardness
The hardness of a material is its ability to resist local deformation, which may come from the indentation of a predetermined geometric indenter on a metal plane under a predetermined load. As a metal, brass is stronger than copper. In terms of hardness index, the hardness of brass ranges from 3 to 4. On the other hand, the hardness of copper in the metal harness diagram shows that brass is the product of different components of copper and zinc. The higher the zinc content, the better the hardness and ductility of brass.

weight
When comparing the weights of metals, water can be selected as the baseline for the specific gravity - the given value is 1. The specific gravity of the two metals is then compared as a fraction of the heavier or lighter density. After doing so, we found that copper is the heaviest, with a density of 8930 kg/m3. On the other hand, the density of brass varies from 8400 kg/m3 to 8730 kg/m3 according to its element composition.

durability
The durability of materials refers to the ability of materials to remain functional without excessive repair or maintenance when facing normal operation challenges within their half life. The two metals show almost the same level of durability in their respective projects. However, compared with brass, copper shows the greatest flexibility.
Although they are all copper materials, because of some basic differences, many copper parts manufacturers will choose to use brass for processing. As more and more brass processing parts are required in the market, it also opens the market for brass machining parts manufacturers.